I'm about to obtain my M.Phil. degree in the field of Computer Science at the University of Sydney (悉尼大学), where I've been studying since 2022. Before delving into research, I enriched my professional experience with a rewarding six-year work in Shanghai. Under the guidance of Prof. Tongliang Liu (刘同亮), I am conducting research on robust deep learning techniques capable of effectively handling imperfect data. This includes scenarios involving data corruption, limited supervision, and small datasets. Additionally, I am investigating the practical applications of these techniques in the field of computer vision.
In 2016, I graduated with a B.Eng. degree in Electronic Information Engineering from Civil Aviation University of China (中国民航大学), mentored by Prof. Hongying Zhang (张红颖). Throughout my career, I've had the privilege to work at several leading companies. By leading diverse projects utilizing C/C++, Python, and Web techniques, I've cultivated a profound understanding of code reliability, reusability, and readability, especially in constructing large-scale systems. These experiences have also equipped me with advanced teamwork strategies, adeptness in communication skills, and expertise in project management.
Hui Kang, Sheng Liu*, Huaxi Huang*, Tongliang Liu. Preprint 2023
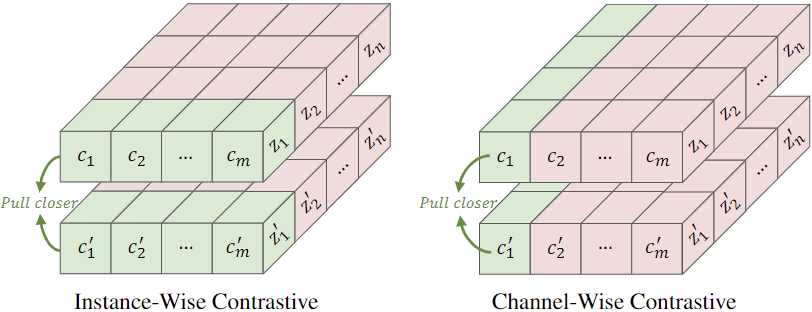
Recent studies show genuine labels can be found in mislabeled data features. To harness this, we introduce CWCL, which discerns true labels from noise by contrasting channels. Unlike traditional methods, CWCL yields refined, accurate features.
Hui Kang*, Sheng Liu*, Huaxi Huang*, Jun Yu, Bo Han, Dadong Wang, Tongliang Liu. Preprint 2023
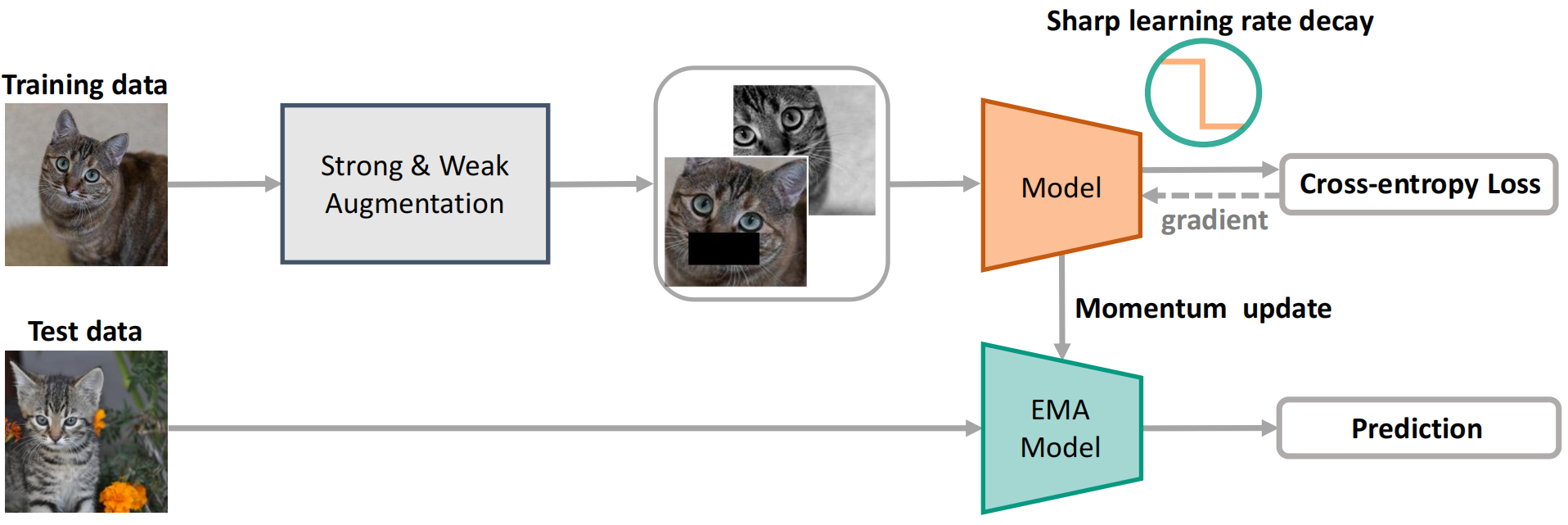
We demonstrate that a simple baseline using ce loss, combined with widely used regularization strategies, can be more effective than intricate algorithms.
Huaxi Huang*, Hui Kang*, Sheng Liu, Olivier Salvado, Thierry Rakotoarivelo, Dadong Wang, Tongliang Liu. ICCV 2023
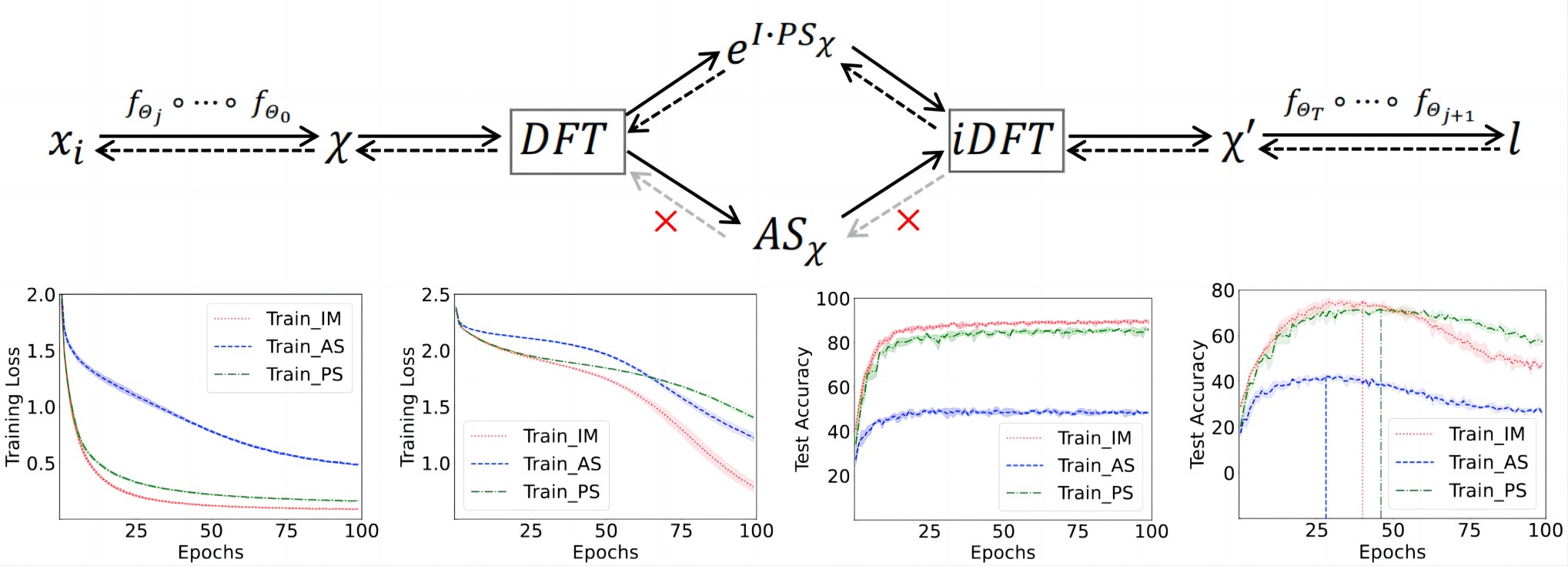
In this paper, inspired by biological research results, we present that phase spectra can enhance the robustness of DNNs to label noise.
Liang Jin*, Jiancheng Yang*, et al, Hui Kang, Jiajun Chen, Ming Li. eBioMedicine (by The Lancet) 2020
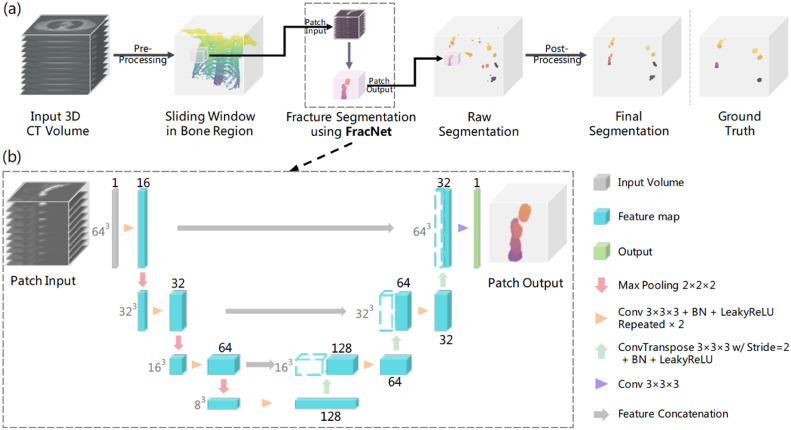
We develop FracNet for detecting rib fractures in CT scans, which achieves high sensitivity with minimal false positives, significantly reducing clinical time.
2022/10 - 2023/09
2012/09 - 2016/06
Linear Algebra: 97/100
Advanced Mathematics: 94/100
Digital Signal Processing: 93/100
C Programming Language: 92/100
First-class Scholarship - Ranking: 5%
Rockwell Collins Scholarship - Ranking: 1/169
Tianjin Government Scholarship - Ranking: 1/169
Second Prize of Beidou Cup China Contest - National
Third Prize of Challenge Cup Tianjin Contest - Provincial
2021/07 - 2022/09
Involved in developing a clinical detection system for intracranial hemorrhage (ICH), which could automatically process images and assess them for hemorrhage within minutes. Trained with thousands of non-contrast CT (NCCT) scans from several hospitals, the system could identify all types of suspected hemorrhage, including intraparenchymal (IPH), intraventricular (IVH), subdural (SDH), epidural (EDH) and subarachnoid (SAH), with a sensitivity of 96%, specificity of 94% and segmentation dice coefficient of 88%.
2019/08 - 2021/06
Developed a clinically applicable automatic deep learning system for rib fractures detection from CT scans, which achieved a high sensitivity of 92.9% with an average of 5.27 false positives per scan and reduced approximate 86% clinical time consuming. A paper was published in eBioMedicine (by The Lancet). A subset of the dataset was open-source to research community, which was the first open large-scale dataset in this application, and we successfully hosted MICCAI 2020 RibFrac Challenge.
2017/04 - 2019/07
Involved in the development of Argus, a prototype adept at detecting lung cancer signs in CT scans using advanced deep learning. Our innovation triumphed at the SAP Labs demo day, securing significant support from SAP's Shanghai development center. Argus now stands as a leading project in SAP's “One Billion Lives” initiative, aiming to tackle global challenges.
Actively involved in the creation of SAPUI5's Gantt Chart control using advanced web techniques. Collaborated with teams for seamless integration with other SAPUI5 components and optimized performance for large-scale applications.
2016/07 - 2017/03
Involved in developing the cockpit flight instrument display system by C/C++ for Boeing company, which was used to display various flight parameters of aircraft graphically.



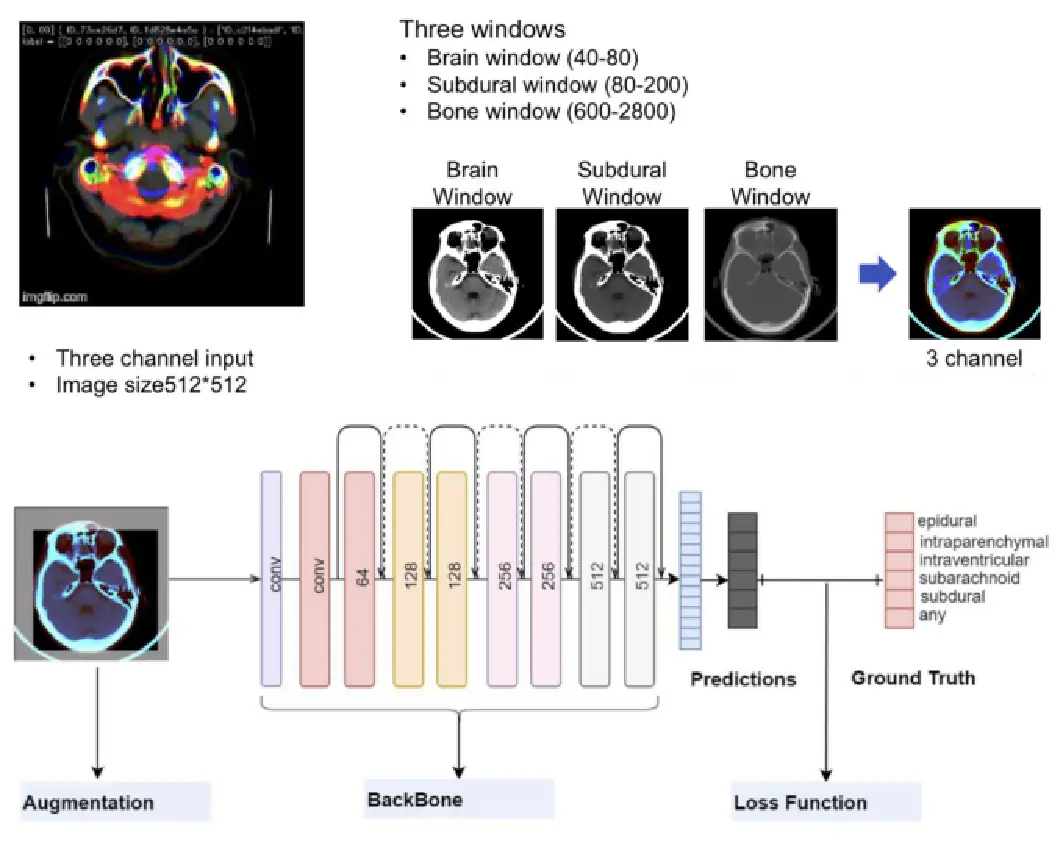
We combined three windows: the brain window (40, 80), subdural window (80, 200), and bone window (600, 2800) to enhance our input. Using transfer learning, we computed classification loss1 to capture intra-slice features from CT scans.
Simultaneously, we harnessed the GAP layer to understand inter-slice correlations in CT scans. By extracting and aggregating features from all slices, we calculated classification loss2, ensuring model also captures broader context.
Utilizing ASPP and attention mechanisms, an advanced 3D CNN segmentation model was devised. This model significantly improved the detection accuracy of diverse pulmonary nodules, considering their varied sizes, shapes, and types.
Addressing false positives in the segmentation model, hard negative mining and multi-model fusion were employed. This approach led to a remarkable decrease in misdiagnoses, cutting down false positives from 146.5 per scan to a mere 5.
Drawing inspiration from the histogram of oriented gradients (HOG) algorithm, we've refined the traditional color histogram into a block-based version, the block-based color histogram offers a robust representation of local features.
Using histogram comparison, we introduced a "confidence map," a probability density indicating a target feature's presence in a new image. We then use the Meanshift algorithm to locate the target in this map.
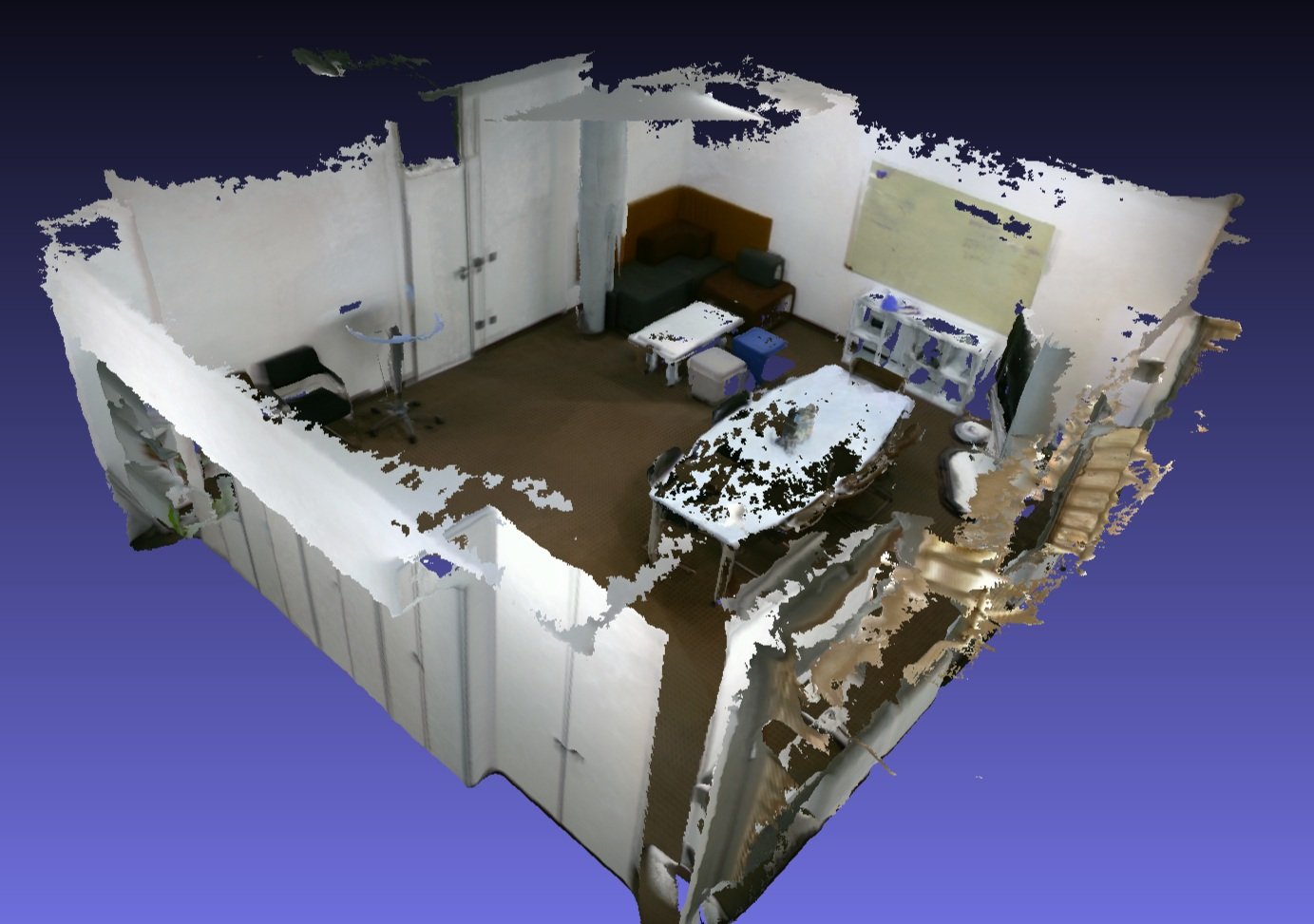
Introducing a rapid and straightforward 3D reconstruction technique leveraging Kinect. We begin by calibrating the Kinect's color camera to access its intrinsic parameters and subsequently align it with the depth camera.
Employing a unique inter-frame filtering method anchored in joint bilateral filtering, we refine the raw depth images. The ICP algorithm then ensures accurate point cloud alignment, culminating in a cohesive 3D point cloud representation.
Languages: Chinese (Mandarin), English
Development Tools: Linux, Docker, Git, Node.js, Numpy, PyTorch
Programming Languages: Python, C/C++, Shell, JavaScript, HTML5, CSS